Adoption of Artificial Intelligence in Smart Cities
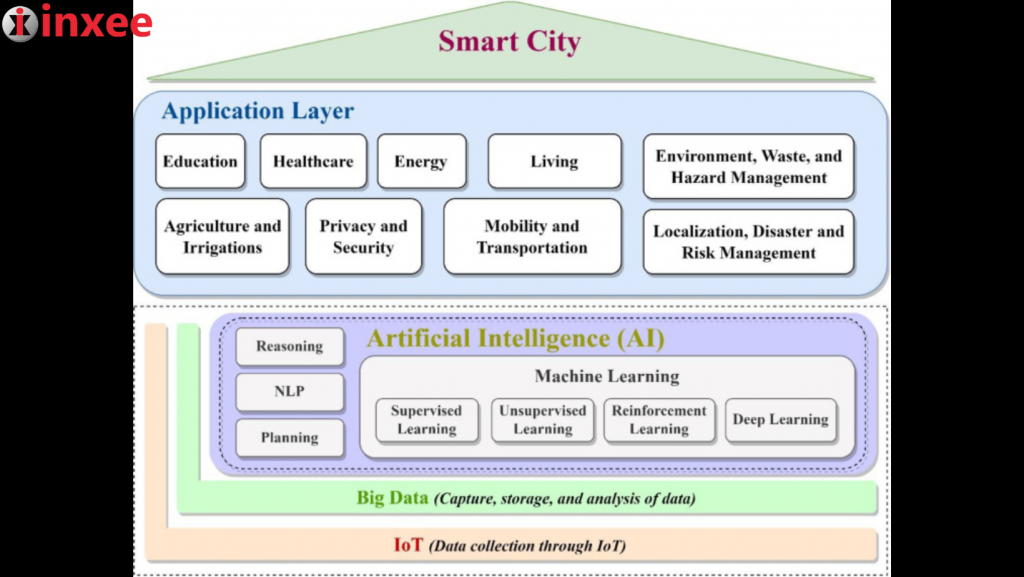
The adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) in smart cities is gaining momentum as cities around the world seek to leverage advanced technologies to address various urban challenges and improve the quality of life for their citizens.
Here are some key areas where AI is being adopted in smart cities:
Urban Planning and Design: AI can analyze large datasets related to population, demographics, traffic patterns, infrastructure, and other factors to provide insights for urban planning and design. AI-powered algorithms can help city planners optimize the allocation of resources, predict demand for services, and optimize transportation routes to reduce congestion and improve efficiency.
Traffic Management: AI can analyze real-time traffic data, including data from sensors, cameras, and other sources, to optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion in cities. AI-powered traffic management systems can dynamically adjust traffic signals, reroute traffic, and provide real-time traffic information to drivers and pedestrians, improving overall traffic management and reducing travel times.
Public Safety: AI can be used for public safety applications such as video surveillance, facial recognition, and predictive analytics to detect and prevent crime, improve emergency response, and enhance overall public safety in smart cities. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data from various sources, such as social media, sensors, and surveillance cameras, to detect patterns and anomalies that may indicate potential safety threats.
Energy Management: AI can optimize energy consumption in smart cities by analyzing data from sensors, smart meters, and other sources to identify patterns and trends in energy usage. AI-powered systems can optimize the operation of street lighting, buildings, and other infrastructure to reduce energy consumption, lower costs, and improve sustainability.
Waste Management: AI can optimize waste management in smart cities by analyzing data from sensors and other sources to optimize waste collection routes, predict fill levels of waste bins, and optimize waste processing and recycling. AI-powered systems can help cities reduce waste, lower costs, and improve sustainability by optimizing waste management processes.
Citizen Services: AI can enhance citizen services in smart cities by providing personalized and automated services through chatbots, virtual assistants, and other AI-powered applications. Citizens can access information, report issues, and receive assistance through AI-powered applications that provide quick and convenient services, improving citizen satisfaction and engagement.
Smart Grids: AI can optimize the operation of smart grids, which are intelligent electricity networks, by analyzing data from sensors, meters, and other sources to optimize energy generation, distribution, and consumption. AI-powered systems can help cities improve energy efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance the reliability and resilience of the power grid.
However, there are also challenges in the adoption of AI in smart cities, including concerns related to data privacy, security, bias, and ethics. It is important for cities to carefully consider these challenges and implement appropriate safeguards and regulations to ensure responsible and ethical use of AI in smart city applications.
In conclusion, the adoption of AI in smart cities has the potential to bring significant benefits in areas such as urban planning, traffic management, public safety, energy management, waste management, citizen services, and smart grids. By leveraging AI technologies, smart cities can become more efficient, sustainable, and citizen-centric, improving the overall quality of life for their residents.









Leave a Reply