June 21, 2023
Artificial Intelligence (AI), cloud computing, edge computing, embedded systems, Home Automation, Industry 5.0, internet of medical things, Internet of Things, iomt, IoT, IoT Devices, Smart City
No comments
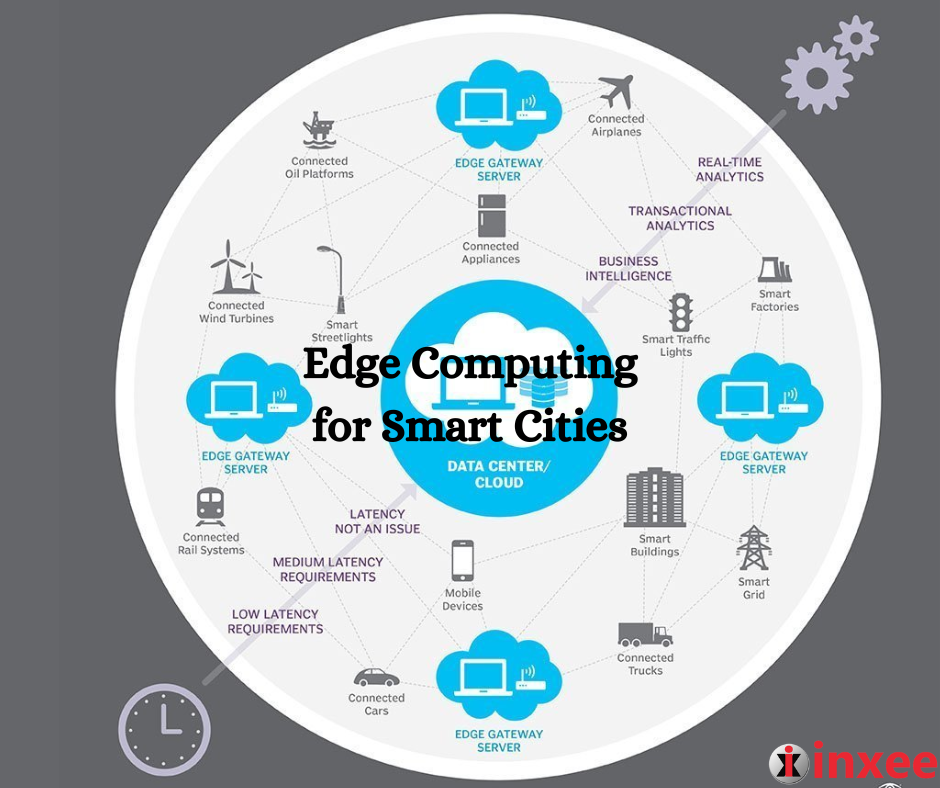
Advantages of Edge Computing for Smart Cities
Edge computing offers several advantages for smart cities, enabling them to overcome the limitations of traditional cloud-centric architectures. Here are some key advantages of edge computing for smart cities:
- Low Latency and Real-Time Responsiveness: Edge computing brings data processing and analytics closer to the data source, reducing the time it takes to transmit and process data. This low latency enables real-time decision-making and responsiveness, critical for applications such as autonomous vehicles, emergency response systems, and smart grid management. By processing data at the edge, smart cities can deliver faster and more immediate services to their citizens.
- Bandwidth Optimization: With the exponential growth of data in smart cities, transmitting all the data to a centralized cloud can lead to network congestion and increased bandwidth costs. Edge computing alleviates this challenge by performing data processing and analysis at the edge devices themselves. Only relevant and aggregated data is sent to the cloud, reducing the amount of data transferred and optimizing bandwidth usage. This helps in improving network efficiency and reducing operational costs.
- Reliability and Resilience: Edge computing enhances the reliability and resilience of smart city systems. By distributing computing resources across edge devices, even in the event of network disruptions or cloud outages, critical services can continue to operate locally. Edge devices can store and process data offline, ensuring uninterrupted service delivery and minimizing the impact of network failures. This is particularly important for applications like public safety, healthcare, and traffic management.
- Enhanced Data Privacy and Security: Edge computing allows sensitive data to be processed and analyzed locally, reducing the need for transmitting it to the cloud. This enhances data privacy and security, as the data remains within the local network, under the control of the smart city administrators. Edge devices can implement robust security measures, such as encryption and access controls, to protect sensitive information and mitigate the risks associated with transmitting data over public networks.
- Scalability and Cost Efficiency: Edge computing enables distributed computing resources that can scale as per the requirements of smart city applications. Instead of relying solely on centralized cloud infrastructure, edge devices can provide additional processing power and storage capacity when needed. This scalability improves resource utilization and cost efficiency, as computing resources can be provisioned based on demand, minimizing the need for overprovisioning and reducing operational expenses.
By leveraging edge computing, smart cities can harness the advantages of low latency, optimized bandwidth, enhanced reliability, improved data privacy, and scalability. These benefits enable them to build resilient and responsive infrastructure, deliver real-time services, and effectively manage the massive amounts of data generated by IoT devices in their urban environments.









Leave a Reply