Challenges of IoMT
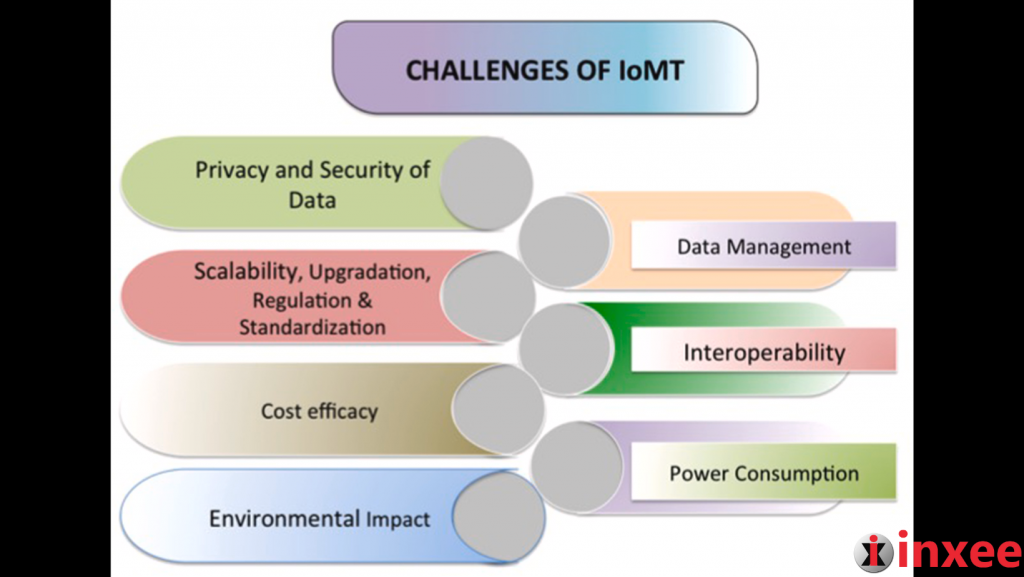
The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) has the potential to revolutionize healthcare, but it comes with its own set of challenges. Addressing these challenges is crucial for the successful implementation of IoMT in healthcare systems. Let’s explore some key challenges and opportunities associated with IoMT:
Privacy and Security of Data: As medical data is generated and transmitted across IoMT devices, safeguarding the privacy and security of patient information becomes paramount. Robust encryption techniques, secure communication protocols, and strict access controls are essential to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access and breaches.
Data Management: IoMT generates vast amounts of data, including patient records, diagnostics, and real-time monitoring data. Effectively managing and processing this data is a significant challenge. Healthcare organizations must develop robust data management strategies, including storage, processing, and analysis capabilities, to derive meaningful insights while ensuring data integrity and accessibility.
Power Consumption: IoMT devices, particularly wearables and sensors, often operate on limited battery power. Optimizing power consumption and extending battery life are crucial to ensure uninterrupted functionality and reduce the burden of frequent battery replacements. Energy-efficient design, power-saving algorithms, and advancements in battery technology are essential to address this challenge.
Interoperability: IoMT involves integrating diverse devices, systems, and platforms from different manufacturers. Seamless communication and data exchange between these devices can be challenging due to variations in data formats, communication protocols, and standards. Developing interoperability frameworks and adopting industry-wide standards are vital to enable seamless integration and data exchange in IoMT ecosystems.
Cost Efficacy: Implementing IoMT solutions can involve significant costs, including device acquisition, infrastructure upgrades, and maintenance. Healthcare organizations must carefully assess the cost-benefit analysis of IoMT deployments to ensure long-term viability and sustainability. Finding cost-effective solutions that deliver tangible value in terms of improved patient outcomes and operational efficiency is crucial.
Environmental Impacts: The growing number of IoMT devices and associated infrastructure can have environmental impacts, such as electronic waste generation and increased energy consumption. Embracing sustainable design principles, responsible disposal practices, and energy-efficient technologies can help mitigate these challenges.
Scalability and Upgradation: As IoMT deployments expand, scalability becomes critical. Healthcare organizations need to plan for future scalability requirements to accommodate the growing number of devices, increased data volumes, and evolving technological advancements. Regular upgradation and replacement of outdated devices and systems are necessary to keep pace with technology advancements.
Regulation and Standardization: IoMT operates in a highly regulated industry, where compliance with regulations and standards is crucial to protect patient privacy, ensure data security, and maintain ethical practices. Developing robust regulatory frameworks and industry standards specific to IoMT is essential to foster trust and drive widespread adoption.
Successfully addressing these challenges requires collaboration among healthcare organizations, technology providers, policymakers, and regulatory bodies. By prioritizing privacy and security, investing in robust data management systems, promoting interoperability, considering cost efficacy, addressing environmental impacts, ensuring scalability and upgradability, and establishing clear regulations and standards, the potential of IoMT can be fully realized. This will lead to improved patient care, enhanced healthcare outcomes, and a more efficient healthcare system in the future.









Leave a Reply