July 10, 2023
5G, Automation, cloud computing, Computer Network, Digital Transformation, Edge AI, edge computing, embedded systems, Fifth Industrial Revolution, Five layer architecture, Industry 5.0, Internet of Things, IoT, IoT Devices, IoT System, Wearables, Wireless
No comments
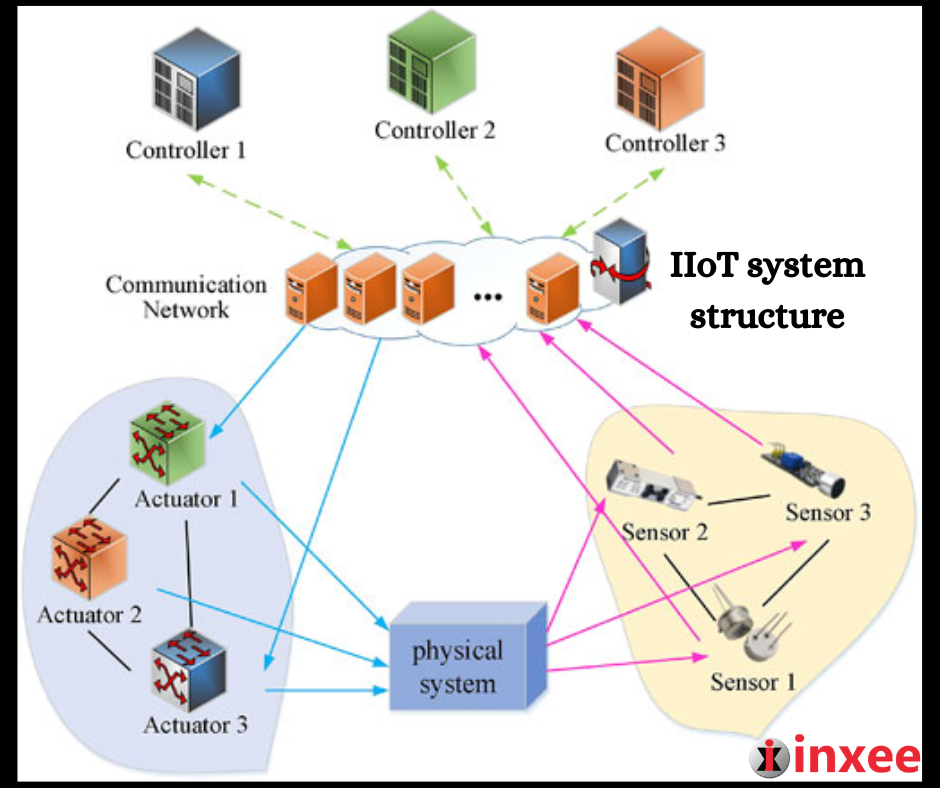
IIoT System Structure
The structure of an Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) system typically consists of several key components that work together to enable the integration and connectivity of devices, sensors, and systems in an industrial environment.
- Devices and Sensors: IIoT systems involve a wide range of devices and sensors that collect data from physical assets, machinery, and equipment. These devices and sensors can include temperature sensors, pressure sensors, motion sensors, actuators, and more.
- Connectivity: IIoT systems rely on various connectivity technologies to enable communication between devices and sensors. This can include wired connections such as Ethernet, as well as wireless technologies like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and cellular networks.
- Edge Computing: In an IIoT system, edge computing plays a crucial role in processing and analyzing data closer to the source, at the edge of the network. Edge computing helps reduce latency, improve real-time decision-making, and minimize data transmission to the cloud.
- Gateways: Gateways act as intermediaries between devices/sensors and the central infrastructure. They collect, aggregate, and preprocess data from multiple sources before transmitting it to the cloud or edge for further analysis and storage.
- Cloud Infrastructure: IIoT systems often utilize cloud-based platforms for storing and processing large volumes of data. Cloud infrastructure provides scalable computing resources, data storage, and advanced analytics capabilities.
- Data Analytics and Visualization: IIoT systems leverage data analytics techniques to extract meaningful insights from the collected data. Advanced analytics tools and algorithms are used to analyze the data and provide actionable information. Visualization tools and dashboards are then used to present the data in a user-friendly format.
- Security and Privacy: Due to the sensitive nature of industrial data, IIoT systems incorporate robust security measures to protect data integrity, confidentiality, and availability. This includes authentication mechanisms, encryption protocols, access controls, and intrusion detection systems.
The structure of an IIoT system is designed to enable seamless connectivity, data collection, analysis, and decision-making in industrial environments. It allows for the integration of devices, sensors, and systems to improve operational efficiency, optimize processes, and enable intelligent automation.









Leave a Reply