MEC ARCHITECTURE
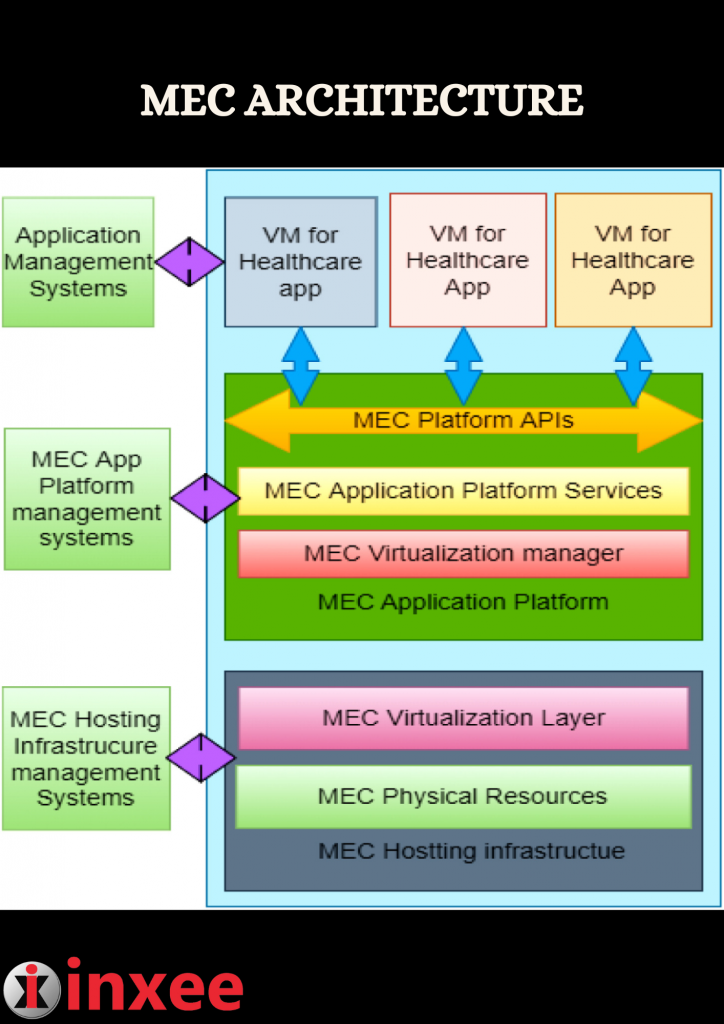
MEC (Multi-access Edge Computing) architecture is a distributed computing framework that brings computational capabilities and services closer to the network edge. It enables low-latency, high-bandwidth, and real-time processing for a wide range of applications. Here is an overview of the MEC architecture:
- MEC Nodes: MEC architecture consists of a network of MEC nodes deployed at the edge of the network infrastructure, typically at base stations or access points. These nodes provide computing, storage, and networking resources that enable processing and analysis of data closer to the end-users.
- Edge Servers: MEC nodes are equipped with edge servers, which are responsible for hosting and executing applications and services. These servers run applications directly at the network edge, eliminating the need to transmit data to centralized cloud servers for processing. Edge servers can be deployed in a distributed manner to serve specific geographical areas or specific network segments.
- Access Network: MEC architecture is integrated with the access network, such as 4G/5G cellular networks or Wi-Fi networks. This integration enables direct communication between the MEC nodes and end-user devices, minimizing latency and improving response times for applications and services.
- Virtualization and Orchestration: MEC architecture leverages virtualization technologies to create virtualized instances of network functions and applications. This enables efficient resource utilization and flexible deployment of services. Orchestration frameworks are used to manage and coordinate the deployment and scaling of virtualized instances across the MEC nodes.
- Connectivity and Backhaul: MEC nodes are connected to the core network infrastructure, typically through high-capacity fiber or microwave links. This connectivity ensures seamless integration with the wider network ecosystem and allows for backhauling of data to central data centers if required.
- Service APIs: MEC architecture provides standardized APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that enable application developers to access and utilize the capabilities of MEC nodes. These APIs allow developers to build edge applications that can take advantage of the proximity and low-latency of MEC infrastructure.
- Analytics and AI: MEC architecture can incorporate analytics and AI capabilities at the edge. This enables real-time data processing, analytics, and decision-making, minimizing the need to transmit data to remote servers. Edge analytics and AI algorithms can provide insights and perform tasks such as data filtering, anomaly detection, and real-time optimization.
The MEC architecture offers several benefits, including reduced network congestion, improved response times, enhanced security and privacy, and the ability to support a wide range of latency-sensitive applications. It enables edge computing capabilities for applications such as augmented reality, video streaming, Internet of Things (IoT), and real-time analytics.
In summary, MEC architecture brings computation and services closer to end-users, enabling faster and more efficient processing at the network edge. It plays a vital role in enabling the deployment of latency-sensitive and real-time applications, contributing to the advancement of technologies such as 5G, IoT, and edge computing.









Leave a Reply