Schematic Representation of Applications of 5G in Healthcare:-
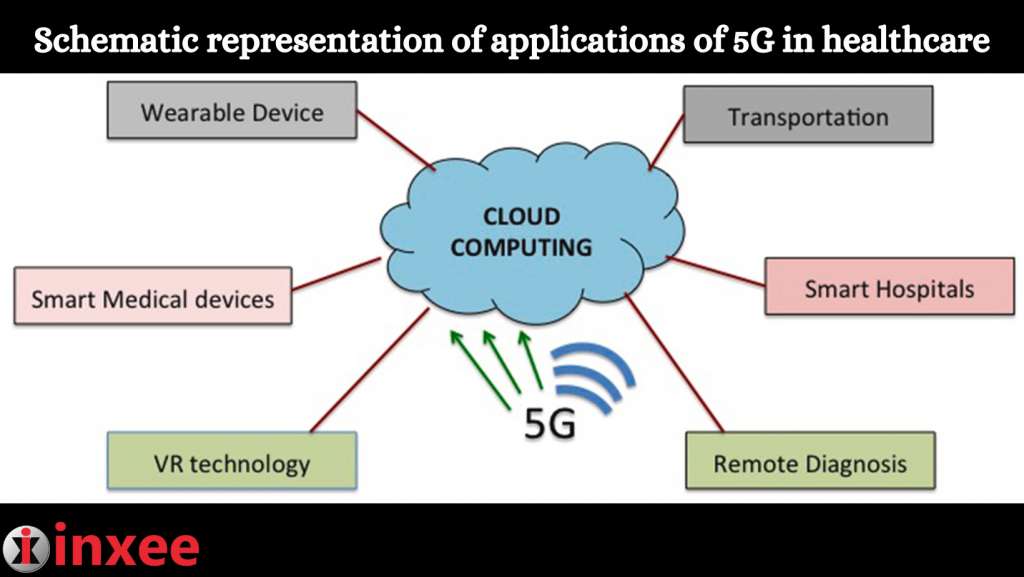
Schematic representation of applications of 5G in healthcare:
- Virtual Reality (VR) Technology: 5G enables high-bandwidth, low-latency connections that are crucial for immersive VR experiences in healthcare. VR technology can be used for medical training, allowing students and professionals to simulate complex procedures, practice surgical techniques, and gain hands-on experience in a virtual environment.
- Medical Devices: 5G connectivity enhances the capabilities of medical devices by enabling real-time data transmission and remote monitoring. Devices such as blood pressure monitors, glucose meters, and ECG machines can transmit patient data to healthcare providers, facilitating remote diagnosis, monitoring, and timely interventions.
- Wearable Devices: 5G connectivity supports the seamless integration and real-time data transmission of wearable devices such as fitness trackers, smartwatches, and biosensors. These devices can collect and transmit vital health information, enabling continuous monitoring, early detection of health issues, and personalized healthcare management.
- Transportation and Emergency Services: 5G connectivity in ambulances, emergency vehicles, and transportation systems enables the transmission of critical patient information to healthcare providers. This allows for faster decision-making, coordination of resources, and timely medical interventions during emergencies or while transporting patients to hospitals.
- Smart Hospitals: 5G technology facilitates the development of smart hospitals, where various devices and systems are interconnected for efficient healthcare delivery. This includes real-time patient tracking, asset management, automated workflows, and optimized resource allocation. Smart hospitals can enhance patient care, streamline operations, and improve overall efficiency.
- Remote Diagnosis and Consultations: With 5G, healthcare providers can conduct remote consultations and diagnosis using high-quality video conferencing and real-time data sharing. This enables access to medical expertise regardless of geographical limitations, improving healthcare accessibility, especially in underserved areas.
- Telemedicine and Telehealth: 5G enables the expansion of telemedicine and telehealth services, allowing patients to remotely access healthcare professionals for consultations, follow-ups, and monitoring. Real-time video interactions, remote monitoring devices, and secure data transmission enhance the delivery of healthcare services to patients in their homes.
- Augmented Reality (AR) in Surgery: 5G connectivity supports the use of AR technology in surgical procedures. Surgeons can use AR overlays to visualize patient anatomy, overlay medical images, and receive real-time guidance during surgeries. This improves precision, reduces risks, and enhances surgical outcomes.
- Data Security and Privacy: 5G networks incorporate advanced security features to protect sensitive patient data. This includes robust encryption, authentication mechanisms, and secure data storage. Data privacy and confidentiality are crucial in healthcare, and 5G technology ensures the secure transmission and storage of patient information.
- Remote Monitoring and Chronic Disease Management: 5G enables remote monitoring of patients with chronic conditions. Connected devices can transmit health data to healthcare providers, who can remotely monitor patients, provide timely interventions, and personalize treatment plans for better disease management.
This schematic representation illustrates the diverse applications of 5G technology in healthcare. From virtual reality for training to remote consultations, smart hospitals, and remote monitoring, 5G is revolutionizing the healthcare industry. It improves access to healthcare services, enhances patient care, and enables efficient healthcare delivery in both urban and remote areas. The integration of 5G in healthcare paves the way for advancements in telemedicine, remote diagnostics, and personalized medicine, ultimately improving patient outcomes and transforming the healthcare landscape.









Leave a Reply