April 26, 2023
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Automation, embedded systems, Smart City, Smart Healthcare, Smart Home, smart hospital, Smart Lighting, Technology
No comments
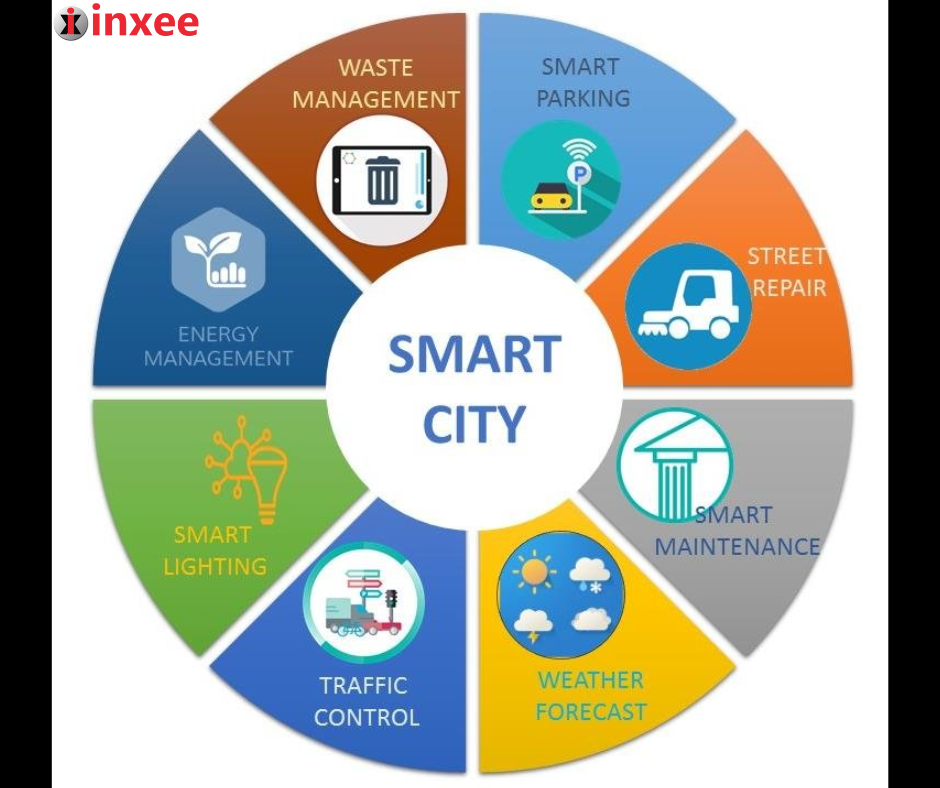
Smart City Paradigm: Key Areas
The key areas of the smart city paradigm include various aspects of urban management and sustainability. Some of these areas are:
- Energy Management: Smart cities employ technology and data analytics to optimize energy generation, distribution, and consumption. This includes the use of smart grids, renewable energy sources, energy storage systems, and demand-side management techniques to reduce energy waste, increase efficiency, and promote sustainable energy practices.
- Waste Management: Smart cities use IoT-based sensors and data analytics to optimize waste collection, recycling, and disposal processes. This includes smart bins, waste monitoring systems, and automated waste collection routes to reduce waste, increase recycling rates, and improve overall waste management efficiency.
- Smart Parking: Smart cities utilize technology to manage parking spaces efficiently. This includes the use of sensors, mobile applications, and data analytics to enable real-time parking availability information, optimize parking allocation, and reduce congestion caused by searching for parking spaces.
- Street Repair and Smart Maintenance: Smart cities utilize technology to monitor and manage the condition of roads, bridges, and other infrastructure assets. This includes the use of sensors, predictive analytics, and remote monitoring to identify and prioritize maintenance needs, optimize repair schedules, and extend the lifespan of urban infrastructure.
- Weather Forecasting: Smart cities rely on accurate and timely weather forecasting to plan and manage various aspects of urban life, including transportation, emergency response, and energy management. This includes the use of data from weather sensors, satellite imagery, and predictive analytics to provide real-time weather information and enable proactive decision-making.
- Smart Lighting: Smart cities use intelligent lighting systems that are equipped with sensors, timers, and automation to optimize energy consumption and improve lighting efficiency. This includes adaptive lighting, smart street lighting, and motion-sensing lights that adjust brightness based on real-time conditions, reducing energy waste and improving public safety.
- Traffic Control: Smart cities employ intelligent traffic management systems that use data from sensors, cameras, and analytics to optimize traffic flow, reduce congestion, and improve transportation efficiency. This includes adaptive traffic signal control, real-time traffic monitoring, and predictive analytics to optimize traffic patterns and reduce emissions caused by congestion.
These are some of the key areas of the smart city paradigm that utilize technology, data analytics, and automation to improve urban management, sustainability, and the quality of life for citizens. By leveraging these technologies, smart cities can achieve greater efficiency, sustainability, and resilience in various aspects of urban life.









Leave a Reply