Three-Tier Architecture for Edge-AI-based Connected Healthcare Systems
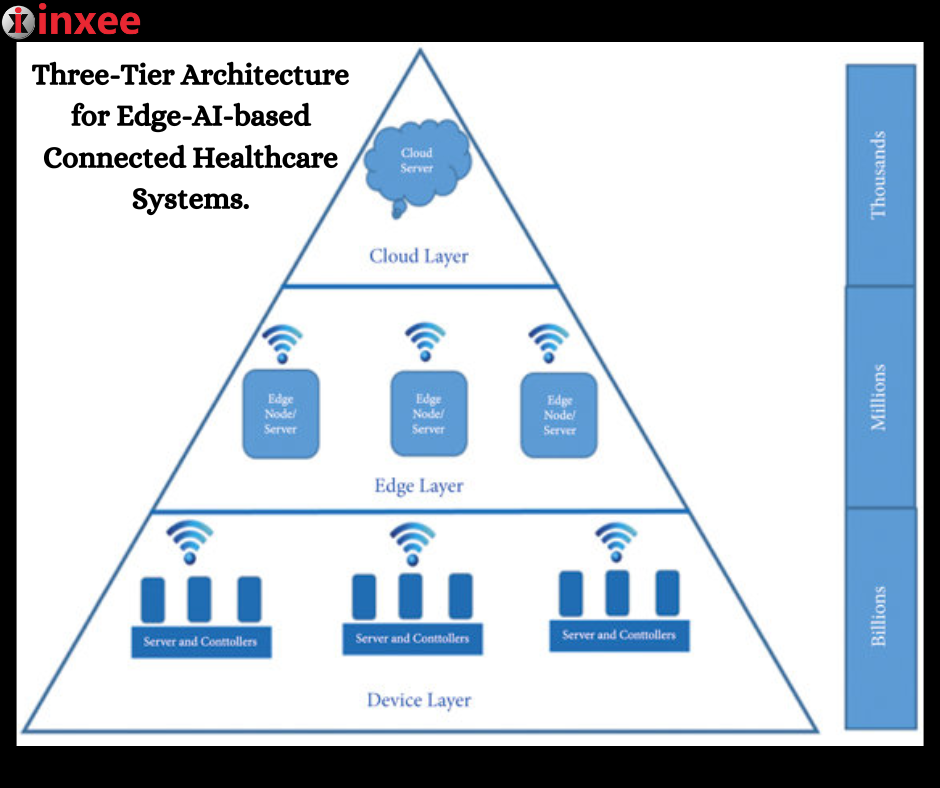
The three-tier architecture for Edge-AI-based connected healthcare systems consists of the following layers:
Cloud Layer: The cloud layer is the top tier of the architecture and involves the use of cloud computing resources. In this layer, data from healthcare devices and sensors is transmitted to the cloud for storage, processing, and analysis. The cloud provides the computational power and storage capacity required for complex analytics, machine learning algorithms, and big data processing. It enables healthcare organizations to leverage advanced AI capabilities and access vast amounts of data from various sources for insights and decision-making.
Edge Layer: The edge layer is the intermediate tier of the architecture and involves edge devices located closer to the data source. These devices include edge servers, gateways, and edge computing platforms. The edge layer performs initial data processing, filtering, and analysis at the edge of the network. It helps reduce latency and network bandwidth by processing critical data locally, allowing for real-time and near-real-time analytics. Edge devices enable faster response times, improved privacy, and enhanced data security by minimizing data transmission to the cloud.
Device Layer: The device layer is the bottom tier of the architecture and includes the various healthcare devices and sensors used for data collection. These devices can include wearables, medical monitors, IoT devices, and other sensors that capture patient health data. The device layer is responsible for collecting and transmitting the raw data to the edge layer for processing and further analysis. It plays a crucial role in providing real-time health monitoring, enabling remote patient care, and facilitating continuous data collection for personalized healthcare interventions.
This three-tier architecture enables Edge-AI-based connected healthcare systems to leverage the power of cloud computing, edge computing, and IoT devices. The cloud layer offers scalable and centralized resources for complex analytics and storage, while the edge layer enables real-time data processing and localized decision-making. The device layer captures vital health data and acts as the interface between patients, healthcare providers, and the system.
This architecture empowers healthcare organizations to deploy AI algorithms, predictive analytics, and machine learning models at the edge and in the cloud. It facilitates real-time patient monitoring, early detection of health issues, personalized treatment recommendations, and population health management. By distributing computing resources across the cloud, edge, and device layers, the architecture optimizes network bandwidth, enhances data privacy and security, and improves the overall efficiency of connected healthcare systems.









Leave a Reply