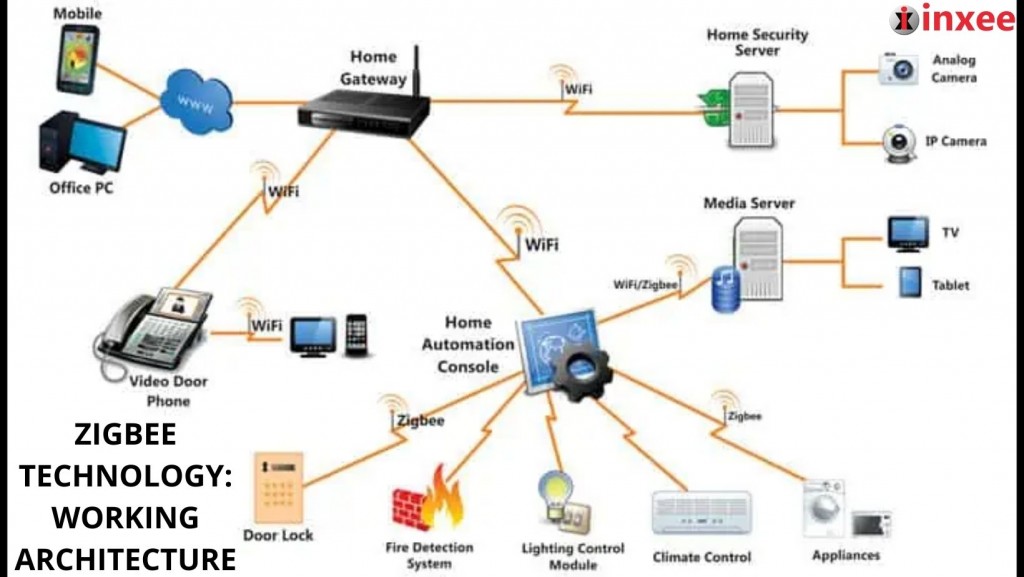
ZigBee Technology: Working Architecture
Zigbee is a wireless communication protocol that is designed to create simple and low-power wireless networks that are capable of connecting to a large number of devices. It operates on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard, which specifies the physical and MAC layer specifications for low-rate wireless personal area networks (LR-WPANs).
Zigbee networks use a star or mesh topology to connect devices. In a star topology, the devices communicate directly with a central coordinator. In a mesh topology, the devices can communicate with each other directly or through intermediate devices.
The communication in a Zigbee network is based on a packet-based protocol. The packet consists of a header and a payload. The header contains information about the destination, source, and type of the packet. The payload contains the actual data that is being transmitted.
Zigbee uses a Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance (CSMA/CA) algorithm to avoid packet collisions. When a device wants to transmit data, it first listens to the channel to make sure it is clear. If the channel is busy, the device waits for a random amount of time before trying again.
Zigbee networks can operate in different frequency bands, including 2.4 GHz, 868 MHz, and 915 MHz. The choice of frequency band depends on the specific requirements of the application.
Zigbee networks are commonly used in home automation, industrial automation, and sensor networks, among others. They offer low power consumption, low cost, and simple implementation, making them an attractive option for many applications.









Leave a Reply